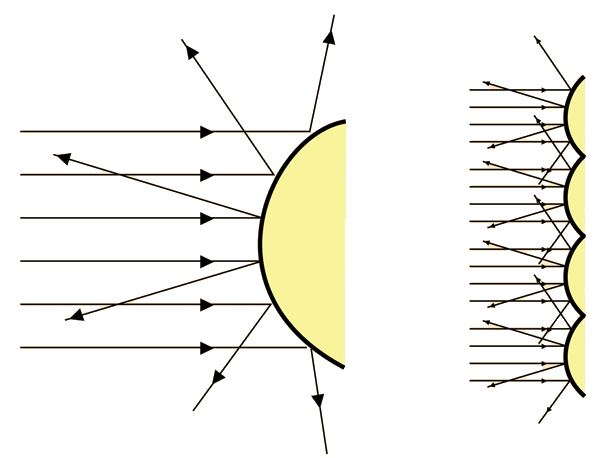
Non-focusing Surfaces
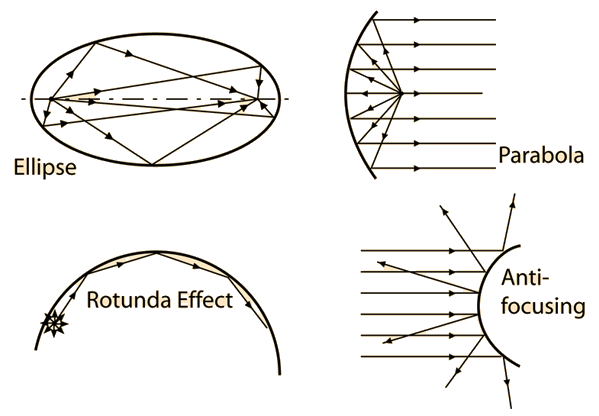
Any time the surfaces of a room focus the sound which is reflected from them, they create spots of high intensity and other spots with low intensity. This is generally undesirable in an auditorium since you want a uniform, evenly dispersed sound to all listeners. | 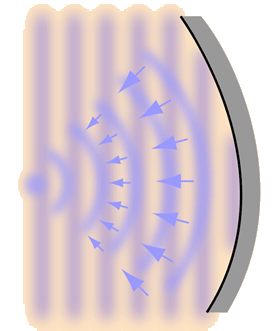 |
Even large flat reflective surfaces are to be avoided because of the prominant reflection which will be produced. Parallel flat walls can produce a pattern of reflections known as a "flutter echo" as the sound waves travel back and forth between the surfaces. Such flutter echoes are often encountered in high school gymnasiums where there are parallel side walls and also a reflective floor and ceiling.
Even dispersion is such an important contributer to good acoustics that it is sometimes desirable to use anti-focusing surfaces in a music making area. Older architecture often had columns, decorative sculpture and woodwork, and other dispersing surfaces. In modern architecture with its flat expanses, it is necessary to design in some anti-focusing properties.
| Archtitectural influences on acoustics | Examples of reflective geometries |
Auditorium acoustics
| HyperPhysics***** Sound | R Nave |