A tree converts disorder to order with a little help from the Sun
The concept of entropy and the second law of thermodynamics suggests that systems naturally progress from order to disorder. If so, how do biological systems develop and maintain such a high degree of order? Is this a violation of the second law of thermodynamics?
Order can be produced with an expenditure of energy, and the order associated with life on the earth is produced with the aid of energy from the sun. The raw materials for the nutrients for life on the Earth are just carbon dioxide and water! The mechanisms of advanced plant and animal life add nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur with most of life's operational mechanisms accomplished with the elements summarized in the mnemonic CHONPS.
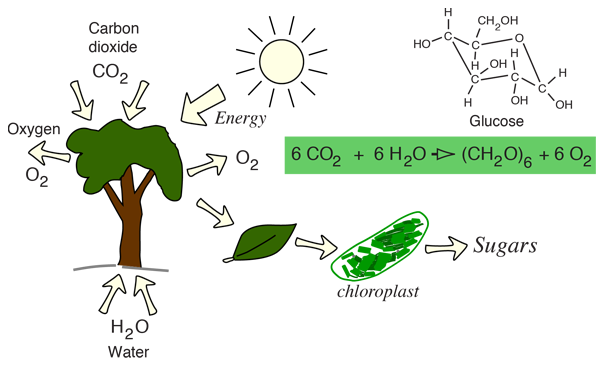
The building materials are in a highly disordered state - gases, liquids and vapors. The tree takes in carbon dioxide from the air, water from the earth as well as a small amount from water vapor in the air. From this disordered beginning, it produces the highly ordered and highly constrained sugar molecules, like glucose. The radiant energy from the Sun gets transferred to the bond energies of the carbons and the other atoms in the glucose molecule. In addition to making the sugars, the plants also release oxygen which is essential for animal life.
The leaves use the energy from the sun in tiny energy factories called chloroplasts. Using chlorophyll in the process called photosynthesis, they convert the sun's energy into storable form in ordered sugar molecules.
As an example of the scope of this process, consider a mature maple tree. It may have 500 pounds of green leaves employed in the process of photosynthesis. Having a leaf surface area of several hundred square meters, it is capable of making some 2 tons of sugar.
The process of photosynthesis in plants stores energy in the plants which can be used for accomplishing work. Some of the energy is used for the synthesis of carbohydrates. These carbohydrates may be simple sugars like glucose or complex combinations of sugars. Some of the common carbohydrates are:
| Cellulose | Long chains of glucose molecules which are fairly linear. They help maintain the plant structure - the wood of trees is primarily cellulose. |
| Starch | More highly branched chains of glucose molecules. They are produced by plants and serve as energy resources for the plants. They can be metabolized by humans and other animals for energy. |
| Glycogen | Even more highly branched chains of glucose, but similar to starches. Used by plants and animals for energy storage. For animals, this glycogen storage is primarily in the muscles. |
In animal systems there are also small structures within the cells called mitochondria which use the energy stored in sugar molecules from food to form more highly ordered structures.
| Order and disorder in biological systems. |
Second law concepts
| HyperPhysics***** Biology | R Nave |