The Trumpet
 |
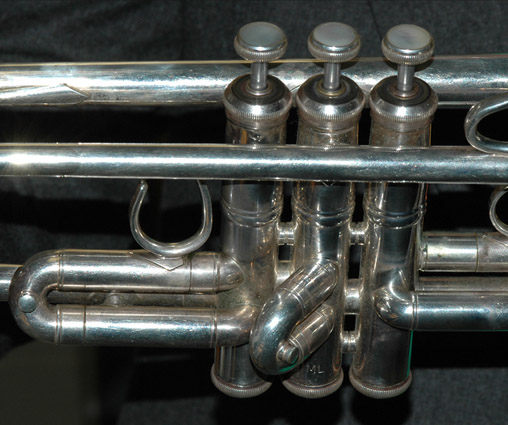
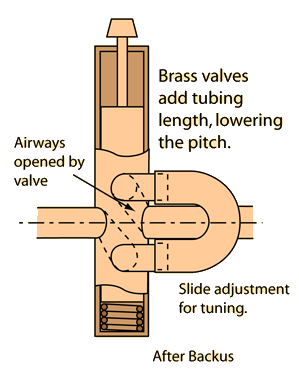
The modern trumpet has three valves and a bore that is partly cylindrical, partly conical. The standard orchestral trumpet, built in B-flat, has a range of about three octaves extending upward from the F-sharp be extending upward from the F-sharp below middle C(F3 sharp = 185 Hz). Models in D, C, and other pitches also exist. |
Music for all models is written as if they were C trumpets (written C sounds B-flat for a B-flat trumpet). This allows players to switch instruments without learning new fingerings.
Those models other than the C are said to be transposing instruments.The cornet is very similar to the trumpet except that it has a conical bore throughout its length while most of the trumpet's bore is cylindrical. Another relative of the trumpet is the flugelhorn , sometimes dubbed the "valved bugle" . It has a mellower sound than the trumpet.
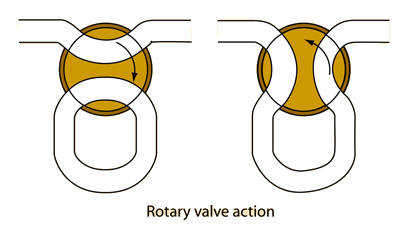
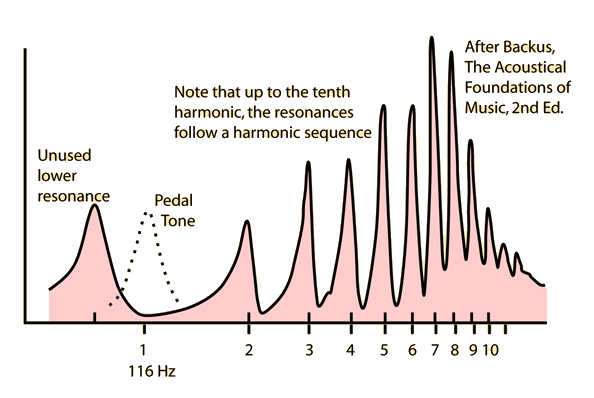
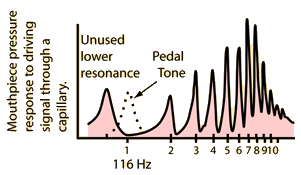
| Use of valves | Producing a harmonic series | Resonance curve |
Brass concepts
Brass instruments
Musical instruments
| HyperPhysics***** Sound | R Nave |