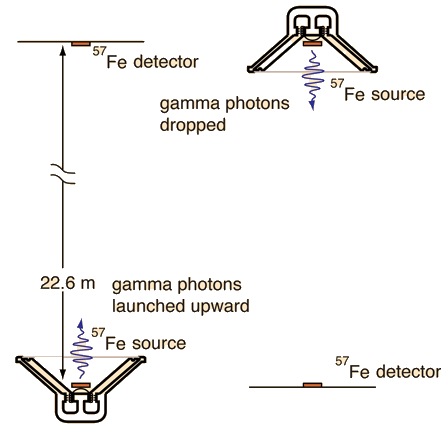
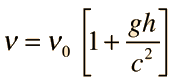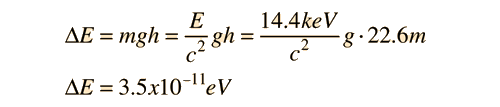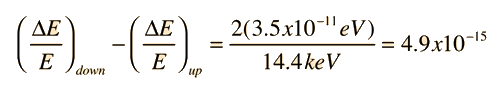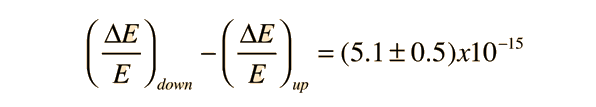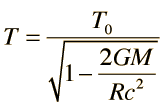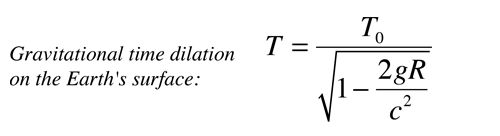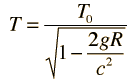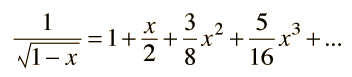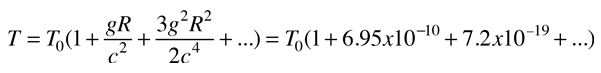Gravitational Red Shift
According to the principle of equivalence from general relativity, any frequency shift which can be shown to arise from acceleration of a radiating source could also be produced by the appropriate gravitational field. If a photon of frequency υ0 is emitted radially outward from the surface of a gravitational mass M, then the photon energy observed at a distance from the mass will be observed to be lower, or "red shifted". If observed at a great distance, we could denote the observed frequency as υ∞. The result of general relativity using the Schwarzschild metric is
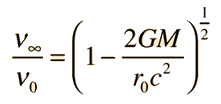
which is valid for even strong gravitational fields. For weak gravitational fields or small displacements in a gravity field, one can make use of the approximation:
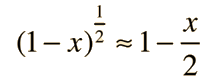
to express the frequency shift between two locations as
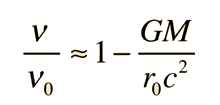
Where υ0 represents a photon emitted closer to the gravitational mass. This form made practical some laboratory experiments using nuclear sources with the gravitational term expressed in terms of the gravitational acceleration g on the Earth's surface.
For the Harvard Tower experiment, the shifts in radiation frequency in the gravitational field were related to the relativistic doppler shift experienced from an accelerating light source.
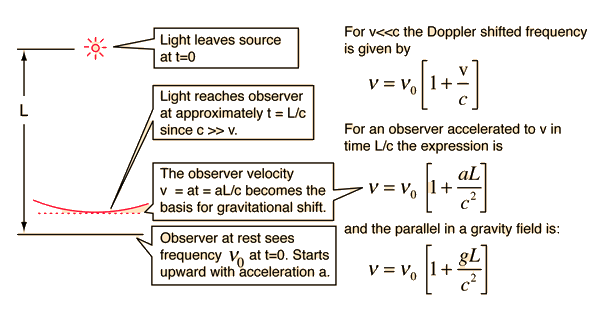
Gravity and the photon
| Harvard tower experiment |
General relativity ideas
References:
Carroll & Ostlie
Sec 17.1
| HyperPhysics***** Relativity | R Nave |