New Horizons Spacecraft
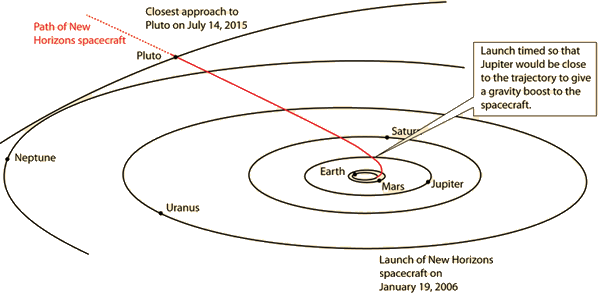
 Credits: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Southwest Research Institute | The New Horizons spacecraft was launched on Jan. 19, 2006 and made its closest approach to Pluto on July 14, 2015. It used a gravity boost from Jupiter in February 2007 to assist in the nine year journey to Pluto. It will continue to send data as it journeys further into the Kuiper Belt. |

The New Horizons spacecraft was launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida aboard and Atlas V rocket.
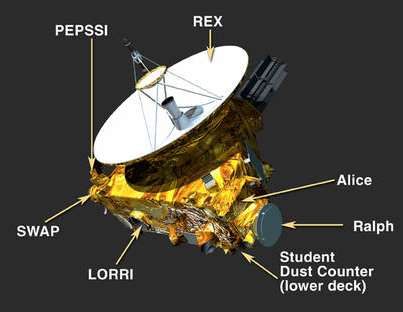
| Ralph | Visible and infrared imager/spectrometer; provides color, composition and thermal maps |
| Alice | Ultraviolet imaging spectrometer; analyzes composition and structure of Pluto's atmosphere and looks for atmospheres around Charon and Kuiper Belt Objects (KBOs). |
| REX | (Radio Science EXperiment) Measures atmospheric composition and temperature; passive radiometer. |
| LORRI | (Long Range Reconnaissance Imager) telescopic camera; obtains encounter data at long distances, maps Pluto's farside and provides high resolution geologic data. |
| SWAP | (Solar Wind Around Pluto) Solar wind and plasma spectrometer; measures atmospheric "escape rate" and observes Pluto's interaction with solar wind. |
| PEPSSI | (Pluto Energetic Particle Spectrometer Science Investigation) Energetic particle spectrometer; measures the composition and density of plasma (ions) escaping from Pluto's atmosphere. |
| SDC | (Student Dust Counter) Built and operated by students; measures the space dust peppering New Horizons during its voyage across the solar system. |
References:
Solar System Illustration
Solar System Concepts
| HyperPhysics********** Astrophysics | R Nave |