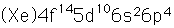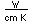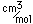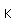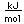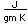Polonium
Polonium was the first element discovered through its radioacivity, having been discovered in 1898 by Marie Curie during their study of the constituents of the mineral pitchblende. Polonium is chemically similar to bismuth and was found as a fraction of the bismuth sulfide in pitchblende ore. Polonium-210 is the only naturally occuring isotope. It has a half-life of 138 days.
Other isotopes of polonium have been produced by bombardment. Most of them disintegrate by emitting alpha particles, and constitute a good source of pure alpha radiation. Such sources are sometimes used to bombard beryllium, which emits neutrons when bombarded by alpha particles.
In some printing and photography equipment where electrostatic buildup is problem, polonium is used to ionize the air to hinder charge buildup.
|