The Thermal Bottleneck
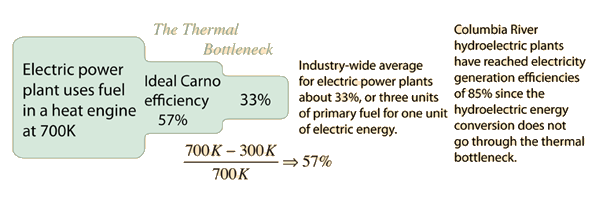
If the first law of thermodynamics says you can't win, then the Second Law of Thermodynamics says you can't even break even. The First Law is essentially a statement of conservation of energy and asserts that you can't get more energy out of a heat engine than you put in. But the Second Law says that no heat engine can use all the heat produced by a fuel to do work. The Carnot cycle sets the ideal efficiency which can be obtained if there is no friction, mechanical losses, leakage, etc., but real machine efficiencies are much less.
Second law concepts
Heat engine concepts
| HyperPhysics***** Thermodynamics | R Nave |