Valine
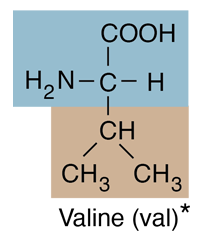 | Valine is an amino acid and belongs to the class which has hydrocarbon R-groups. Valine is strongly hydrophobic, and tends to contribute to closeness in protein folding as they gather together to avoid water. It is found in many proteins, mostly in the interior of globular proteins helping to determine three-dimensional structure. |
In sickle-cell disease, a single glutamic acid in beta-globin is replaced with valine. Because valine is hydrophobic, whereas glutamic acid is hydrophilic, this change makes the hemoglobin prone to abnormal aggregation.
Valine, like other branched-chain amino acids, is associated with insulin resistance: higher levels of valine are observed in the blood of diabetic mice, rats, and humans. In humans, a protein restricted diet lowers blood levels of valine and decreases fasting blood glucose levels.
* Amino acids which are essential amino acids which cannot be made by the human body and, therefore, must be obtained in the diet.
| Valine wiki |
Biochemical concepts
Chemistry concepts
Reference
Tillery, Enger and Ross
Ch 14
Ahern
| HyperPhysics*****Chemistry *****Organic Chemistry | R Nave |